NATIONAL SECURITY: FROM COLD WAR TO CODE WAR
Cyber espionage doesn’t mean the direct destructive activity but the mala-fide intentions for the penetrations of hacker’s computers to obtain information for intelligence purposes. obtained can be used for military operations. This may affect the sovereignty of a nation and can affect the government’s policies and decisions. Spies in this espionage are termed as hackers. They no need to travel the enemy country and can collect the top-secret information by just hacking the other nation’s server. In this, chances of exposure are also very less. top-secrets of a state can be obtained through cyber espionage.
22 April 2022 • 12 min read
Author: Eccentric
Mikhail S. Gorbachev, the general secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union launched the dual program of “perestroika” and “glasnost” which introduced drastic changes in the economic policies, internal affairs and international relations of Soviet Union. These two policies are largely responsible for the collapse of the Soviet Union on December 21, 1991, whose consequences bought a paradigm shift in its ideological and economic policies. Due to this, USA’s political commentators concluded that America had conquered Russia, signaled the end of the Cold War, which started at the end of World War II.
From Cold War to Code War
The word Cold War traces its etymology from the French word “la guerre froide” which means “Cold War”. The term is used since, there was no fighting directly between the two sides (USA USSR) involved in the conflict, but was a state of geopolitical tension after World War II. But in this digital era of internet world, after 27 years of the end of Cold War, world is facing a new kind of warfare which exists but intangible, i.e. ; Code War.
Cold War has given way to a in which cyber weapons can be used with unpredictable consequences. As in Cold War, the agenda and the participating nations are well known but there is no such clear information regarding code war. It may consist of state or non-state actors or may be an individual also. It’s not only country v/s country but country v/s company, company v/s company, country v/s individual or individual v/s company.
Cyber war is fait
Today’s age is the age of information. Timely information is everything. It is prevailing all around us. Around the globe people are connected through internet, no matter whether they are in office, public transport, parks, streets, restaurants etc. And hackers are well aware of this fact. The first hacking incident takes place in 1903. First paper on cyber security threats was published in 1967 by Willis Ware (then US policy adviser). Ronald Reagan, in 1983 had helped to create the first (US) national security policy directive on information systems security. In the 21st century, Cyberspace is the new domain of warfare and most of the nations are ill prepared. In cyberspace there is no longer a military world and a civilian world. The boundaries have merged. In both the world wars, technological advancements played a significant role. From the era of cold war to code war, cyber skirmishes will become the reality and a part of diplomatic parlance.
CODE WAR

CYBER ATTACKS:
An Opportunity which is everywhere for hackers
Cyber Attacks can be defined as, intended actions on computer systems or networks to achieve 4Ds, i.e. disrupt, deceive, degrade and destroy.
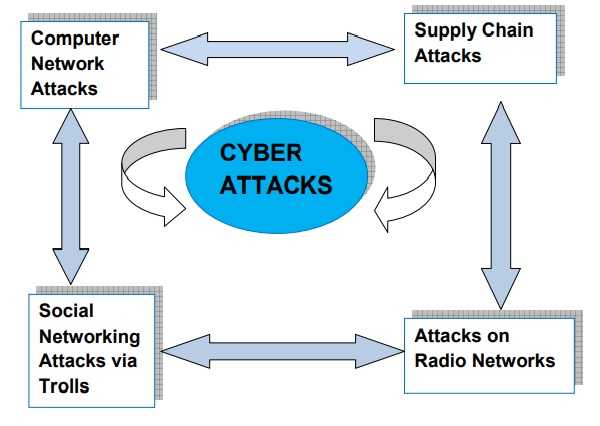
Cyber Attacks are easy to perform and the results may be from abrupting or defacing or maligning a website or stealing data and intellectual property or can be espionage which can disrupt critical services. It can be launched against the infrastructures of nations like banking, power supply, transportation system, telecommunications etc. Hackers can take advantage of lacunae in such systems and can thus disable/disrupt the essential services. An attack on banking services can not only affect a single person but can affect the economy of a nation. In a similar manner simultaneous attacks on power supply or air transportation system or railway networks or on our communication system can create a war like situation. This is Code War and the effects are similar as one can achieve by nuclear attacks or weapons of mass destruction.
Cyber Attack thus raises following questions for the affected country/company/individual
Whether it is a deliberate attack
Who launched it
How to prove the above two questions
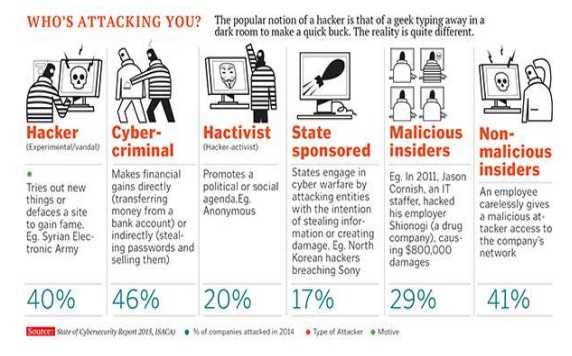
It is extremely difficult to provide the concrete answers for the above questions in cyber world.
Cyber Espionage
Cyber espionage doesn’t mean the direct destructive activity but the mala-fide intentions for the penetrations of hacker’s computers to obtain information for intelligence purposes. Information thus obtained can be used for military operations. This may affect the sovereignty of a nation and can affect the government’s policies and decisions. Spies in this espionage are termed as hackers. They no need to travel the enemy country and can collect the top-secret information by just hacking the other nation’s server. In this, chances of exposure are also very less. top-secrets of a state can be obtained through cyber espionage.
Cyber Warfare
“The fifth domain of warfare”
The Economist Magazine
“Actions by a nation-state to penetrate another nation’s computers or networks for the purposes of causing damage or disruption.
Richard A Clarke (Former US Security Expert)
In this digital era of 21st century, cyberspace must be considered as a new domain in warfare as military operations as land, sea, air, and space. Few known cases of cyber warfare are mentioned below-
Soviet spies stolen the computer code from a Canadian company. The code was further modified by the CIA which changed the pump speeds abruptly causing explosion in the Soviet Gas pipeline.
Iraqi anti-aircraft guns started malfunctioning due to a computer virus named AF/91. It was installed on “Moonlight Maze” - U.S officials discovered a pattern of probing computer networks at high profile places like Pentagon, NASA, Energy Department, private
universities and research labs during this period. It breached the maps of military installations, troop configurations and military hardware designs. “Titan Rain” - Chinese attack on U.S. computer. It is covered by proxy, zombie computer, spyware and virus infected, hence real identities still remain unknown.
Cyber warfare was used against Hezbollah also.
Russian Hackers and scientists operated on the behalf of several countries to attack Israel Defence Force.
China was involved in cyber war and carrying cyber-attacks on India, Germany and the United States.
(A cyber spy network), via servers mainly based in China has secretly collected the classified documents from government and private organizations in 103 countries. A well planned and coordinated cyber attacks against major government, news media, and financial websites in South Korea and the United States. “Operation Aurora” - A cyber attack in 2009 which was first publicly disclosed by Google on January 12, 2010. It was claimed to be originated from China. The attack had seriously affected the network systems of Adobe Systems, Juniper Networks and Rackspace.
- Affected Iran's Natanz nuclear enrichment facility. Citi Bank says 360,000 of its were accounts hacked in cyber attack.
10,000 Indian government and military emails hacked despite a warning from the country’s cyber security agency. The attack came on 12 July, four days after the government was warned by the National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre (NCIIPC), part of the National Technical Research Organisation (NTRO), that some sophisticated malware was spotted targeting specific individuals and organisations.
Singapore cyber attacks The 2013 Singapore cyber attacks were a series of hack attacks initiated by an anonymous organisation, represented by a member known by the online handle
The Messiah
The cyber attacks were partly in response to web censorship regulations in the country, specifically on news outlets. On 12 November 2013, James Raj was charged in Singapore court as the alleged
The Messiah
A series of cyber attacks on major U.S. companies.
FBI portal breach - A portal used by U.S. police and the FBI to share intelligence and arrest suspects was hacked and data on arrestees stolen. While the FBI didn’t announce figures on how many people were
affected, this attack is thought to be one of the biggest law enforcement hacks.
Indian Debit Card Hack 32 lakh debit cards belonging to various Indian banks were compromised resulting in the loss of Rs 1.3 crore in fraudulent transactions as per NPCI. WannaCry ransomware attack
The WannaCry ransomware attack was a worldwide cyberattack by the WannaCry ransomware cryptoworm, which targeted computers running the Microsoft Windows operating system by encrypting data and demanding ransom payments in the Bitcoin crypto currency. The attack began on Friday, 12 May 2017 and within a day was reported to have infected more than 230,000 computers in over 150 countries.
Cyber attacks in India
Two south Indian banks along with few Delhi based manufacturing companies, the headquarter of a big corporate house were affected in WannaCry ransomware attack. More than 100 PCs of Andhra Pradesh police have also been affected. This cyber attack was carried out using a malware called Wanna Decryptor or WannaCry. This is a “ransomware“, a digital extortion system that locks down systems by encrypting the data on it, only to decrypt and release it back for a ransom amount. A worrying fact is that 70% of Indian ATMs still use the outdated version of Windows XP which acts as a major carrier for the WannaCry ransomware cryptoworm.
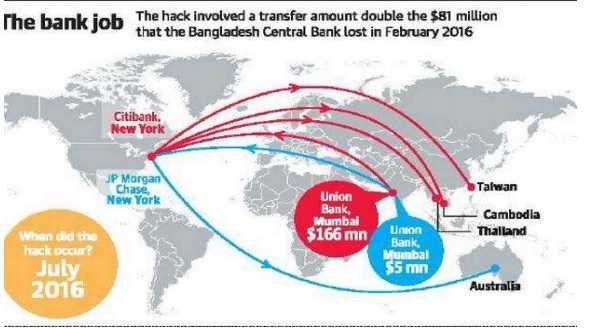
An illegitimate money transfer of $166 million in July 2016, happened from Union Bank Of India. This hack involved a transfer double the size of the Bangladesh Central Bank that lost $81 million February 2016.
Cyber Security Challenges
“The only computer that’s completely secure is a computer that no one can use.”
Cyberspace consists of various IT networks, computer resources and mobile devices connected to Internet across the globe. A nation’s cyberspace is subset of the global cyberspace; it can never be isolated to define its boundaries since cyberspace is borderless. This makes cyberspace unique. Unlike the physical world, limited by geographical boundaries in space—land, sea, river waters and air, cyberspace is continously expanding. Due to increase in internet penetration growth of cyberspace is also increasing, since its size is proportional to the activities that are carried through internet.
Nowadays, nations are investing heavily in their Information and communication technology infrastructures by providing higher bandwidths, to integrate national economies with the global marketplace and to enable citizens or “netizens” to access more and more e-services. Due to increase in the security problems, there is increased emphasis on investment in the security of cyber infrastructure. Core Internet protocols are insecure, and an explosion of mobile devices continues to be based on the same insecure systems. This is adding up to increased usage of the Internet in more vulnerable cyberspace.
Protection of critical infrastructure operations has emerged as a major challenge. This is because trillions of dollars move through the networks every day involving a broad range of activities, including e-commerce, e-governance, travel, hospitality, health care, and general communications. Electricity distribution, water distribution, and several other utility services are based on Information and communication technology infrastructures.
Fixing Ownership and Responsibility
Major and critical infrastructures in information and communication technology are largely owned and operated by the private sector. But the question arises is that their security is only the private sector’s responsibility? Does this mean that government has a lesser role in this segment? These are some of the important cyber security issues that nations are grappling with. At an organizational level, too, cyber security is not merely a technology issue, but a management issue. This is grounded in enterprise risk management, which calls for an understanding of the human, process, legal, network, and information and communication technology security aspects.
Roles and responsibilities of each of the parties (private sector and public sector) need to be clearly defined. Also, governments need to establish the appropriate policy and legal structures regarding information and communication technology. Few nations, such as the United States, have favored for a market-based, voluntary approach to industry cyber security as part of the National Strategy to Secure Cyberspace. But this has not worked entirely, because security investments made by industry, as per their corporate needs, are not found to be commensurate with the broader national interest.
Since, multiple agencies are involved in securing information and communication technology infrastructure which includes private operators for their respective pieces of the infrastructure. Their efforts needs to be firmly coordinated through an integrated command-and control entity, which should serve as a unifying structure and must be accountable for cyber security.
From Digital India to Secure India Digitally
Digital India program was launched on 2 July 2015 by Prime Minister Narendra Modi. The vision of Digital India programme is inclusive growth in areas of electronic services, products, manufacturing and job opportunities etc. and it is centred on three key areas – Digital Infrastructure as a Utility to Every Citizen, Governance Services on Demand and Digital Empowerment of Citizens. But this program will become successful in its true spirits when we become a digitally secure nation. India should take certain measures to safeguard itself digitally. Indeed, our country’s approach to this will be pivotal. Appointment of Gulshan Rai as a national cyber security coordinator in the PMO is a step in the right direction.
In order to secure India from acts of state and non-state actors, a protocol for grievance redressal in international forums must be suggested. The computer emergency response team (CERT) should be strengthened and must be aligned with military and foreign affairs operations. The government’s cyber security policy should be revisited on timely basis and must be implemented in mission mode. Also, a global charter of digital human rights will prove a boon in this segment.
Since, it is good to build own capabilities and protect nation critical infrastructure, it is also important to have International cooperation for securing borderless cyberspace. When it comes to tracking cyber criminals, it is not only the laws dealing with cyber crimes that must exist in various countries, but the collection of appropriate cyber forensics data in various jurisdictions and their presentation in courts of law, which are essential to bring criminals to justice in sovereign countries. Global service providers such as Google, Microsoft, Twitter, Yahoo, and Facebook to cooperate with law enforcement agencies. There should be acceptable legal norms for dealing with cyber crimes regarding territorial jurisdiction, sovereign responsibility, and use of force to reconcile differing national laws concerning the investigation and prosecution of cyber crimes, data preservation, protection, and privacy. This should address the problem of existing cyber laws that do not carry enforcement provisions.
While covering digital security and securing our nation from cyber war, one should also consider the ethical values of data privacy. Personal data shall be obtained only for the sake of nation’s security not for fulfilling the purpose of any individual.
Subscribe to Pasmanda Democracy
Get the latest posts delivered right to your inbox.
Politics
Share:
